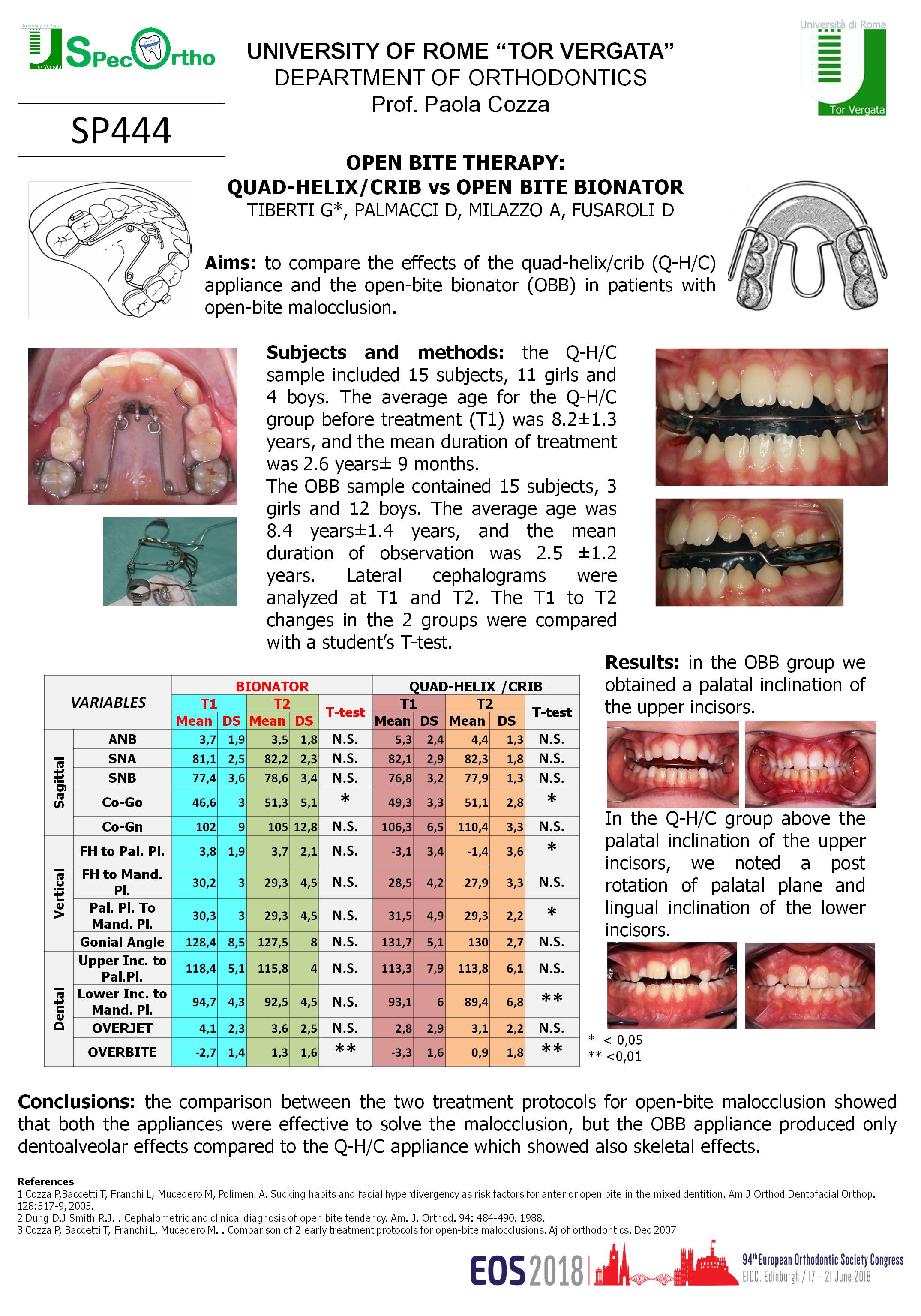
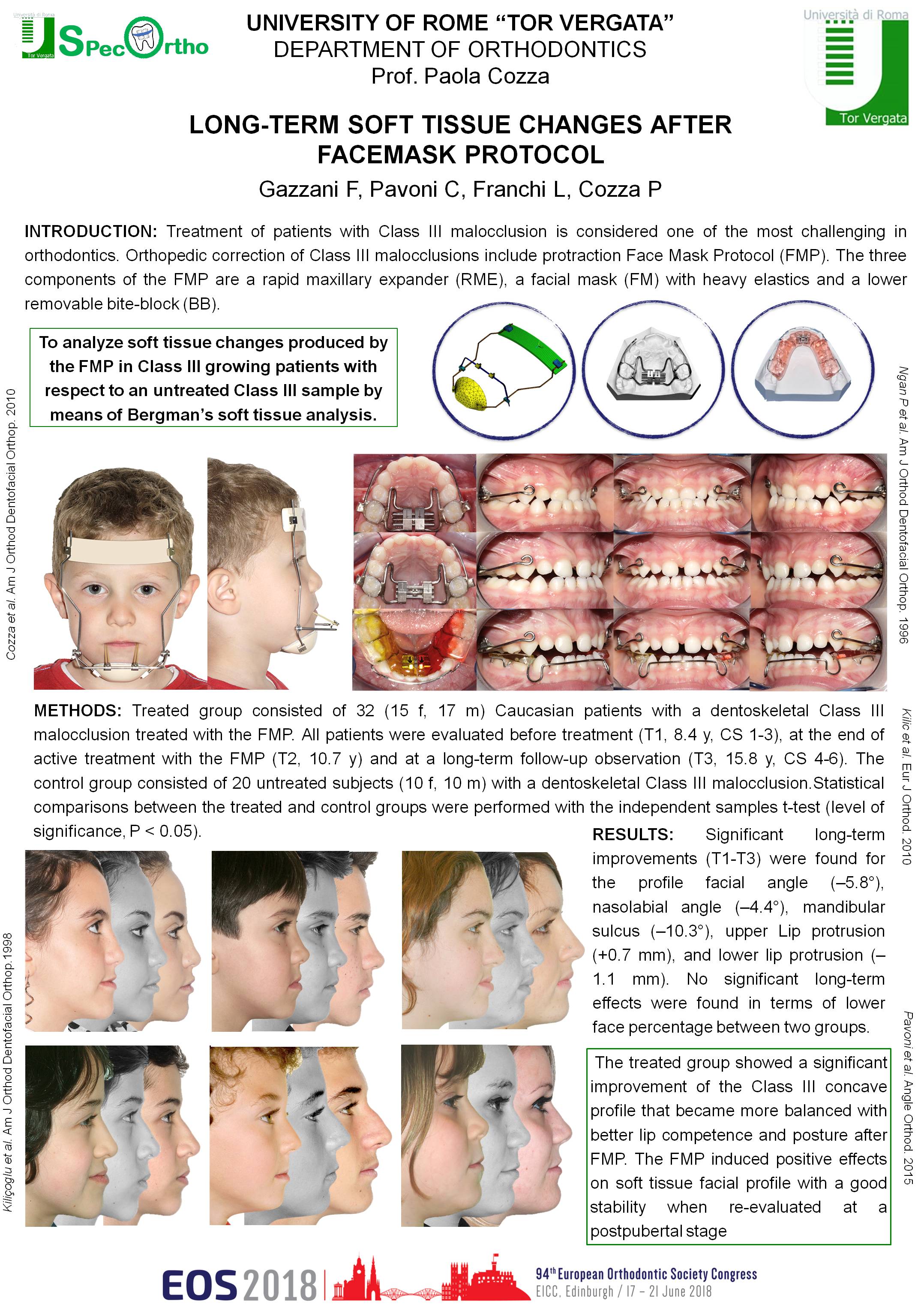
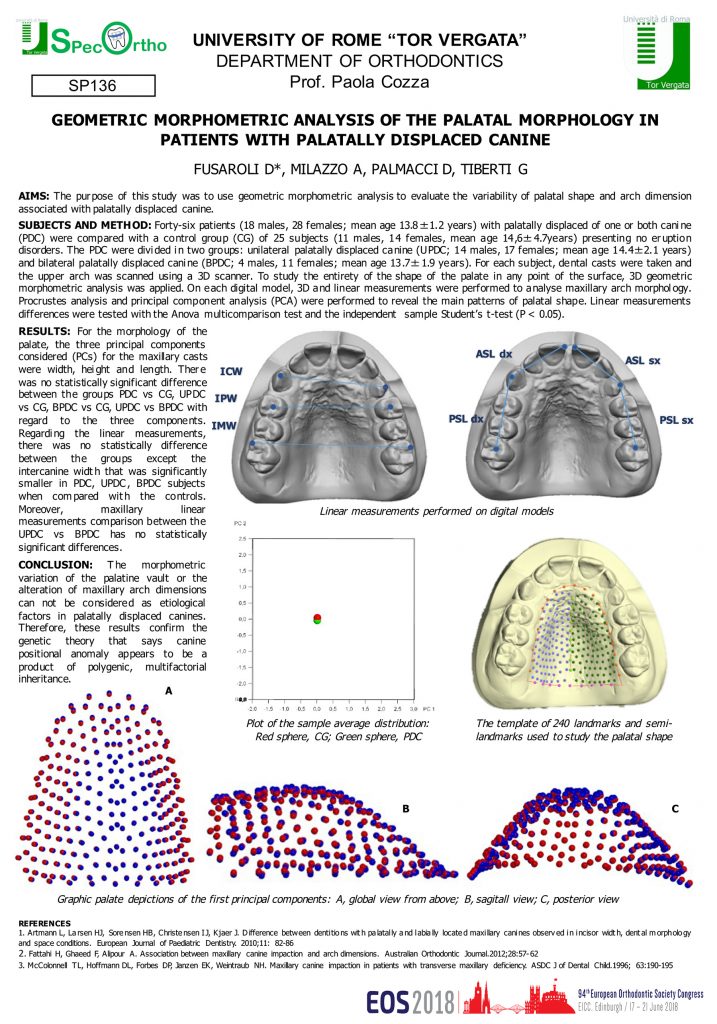
Associations between displaced maxillary canines and tooth agenesis: a cross-sectional radiographic study in a large sample.
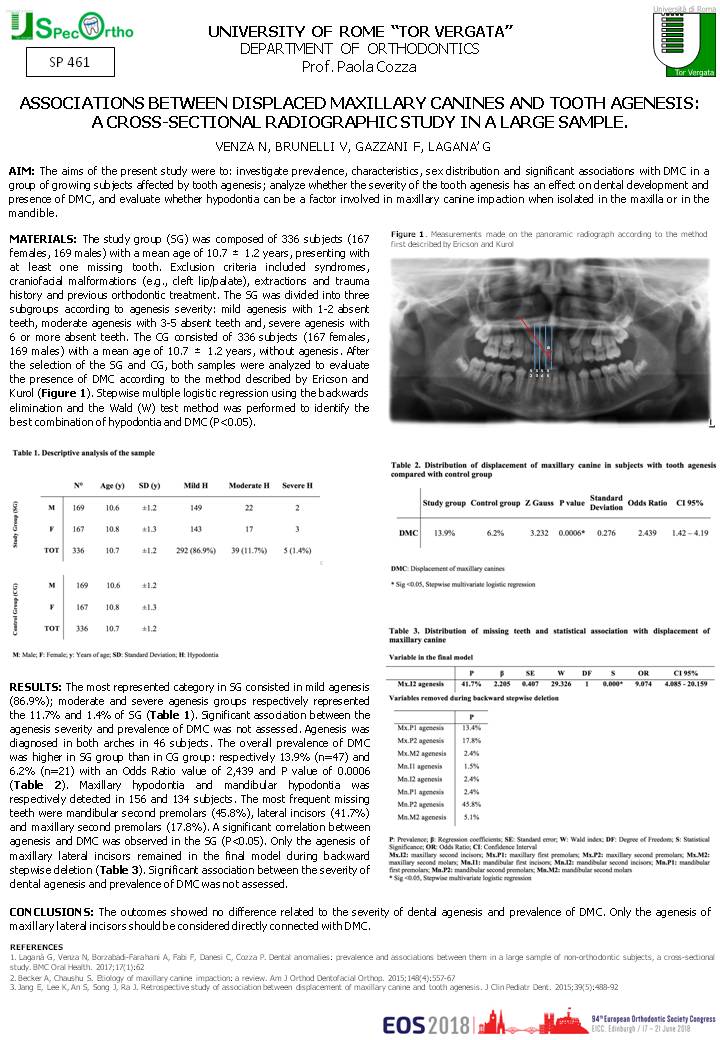
AIM: The aims of the present study were to: investigate prevalence, characteristics, sex distribution and significant associations with DMC in a group of growing subjects affected by tooth agenesis; analyze whether the severity of the tooth agenesis has an effect on dental development and presence of DMC, and evaluate whether hypodontia can be a factor involved in maxillary canine impaction when isolated in the maxilla or in the mandible.